The Ultimate Guide to Sizing Your Industrial Air Compressor: How to Choose the Right Capacity & Avoid Costly Mistakes
Why Proper Compressor Sizing Matters
When it comes to industrial air systems,
bigger isn’t always better, and neither is too small. Choosing the wrong compressor size, whether too large or too small, can lead to a cascade of negative consequences, including wasted energy, reduced productivity, premature equipment wear, and unnecessary operational costs. The initial investment in an air compressor is significant, but the ongoing operating costs, primarily energy consumption, far outweigh the initial purchase price over the lifespan of the equipment.
In fact, the
U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) rigorously researches and reports on industrial energy efficiency, consistently highlighting that improperly sized compressors can waste up to 30% of total energy consumption in manufacturing facilities. To put this into perspective, for a medium-sized manufacturing plant, this could translate to tens of thousands of dollars lost each year due to inefficiency alone. This financial drain directly impacts the bottom line and reduces a company’s competitiveness. Furthermore, an undersized compressor can’t meet demand, leading to production slowdowns and potential equipment damage from being constantly overworked. Conversely, an oversized compressor cycles on and off more frequently, which increases wear and tear on components, shortens the lifespan of the unit, and still consumes excessive energy during its operational cycles.
That’s why partnering with specialists is crucial. Industrial Air Services Texas (IAS) stands out in the industry for its expertise in helping businesses select and size the right compressor system for their unique operations. With decades of experience spanning air systems design, meticulous installation, and comprehensive maintenance, IAS ensures that your equipment not only delivers peak performance and reliability but also operates with optimal energy efficiency, preventing overspending on power and maintenance. Their approach involves a thorough assessment of your specific air demand, considering factors like current and future needs, operational hours, and the specific applications for compressed air within your facility. This tailored approach guarantees a solution that is both robust and cost-effective.
The body content of your post goes here. To edit this text, click on it and delete this default text and start typing your own or paste your own from a different source.

Step 1: Identify Your Air Demand (CFM)
The foundation of compressor sizing starts with understanding your airflow requirements, measured in CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute). Each pneumatic tool or process in your facility consumes a specific amount of air. Add up the CFM of all tools that may run simultaneously, and include a small safety margin.
Example:
- Paint sprayer: 8 CFM
- Impact wrench: 5 CFM
- Sandblaster: 20 CFM
Total: 33 CFM + 25% margin = ≈ 41 CFM
IAS Texas offers on-site air demand audits using digital flow meters to determine your exact CFM usage. This ensures your compressor is perfectly matched to your facility’s needs—no guessing, no wasted energy.
Determining Airflow Requirements (CFM)
The cornerstone of selecting the right industrial air compressor lies in accurately determining your airflow requirements, meticulously measured in Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM). This foundational step is critical to ensure optimal performance, energy efficiency, and to prevent costly mistakes associated with undersized or oversized systems.
Calculating Your Facility's Air Consumption:
To precisely calculate your facility's air consumption, you must meticulously identify every pneumatic tool and process that relies on compressed air within your operations. Each of these applications consumes a specific, quantifiable amount of air. The key is to:
- List All Pneumatic Tools and Processes: Create a comprehensive inventory of every device that will draw compressed air. This could range from small hand tools to large-scale industrial machinery.
- Determine Individual CFM Requirements: For each item on your list, ascertain its individual CFM consumption. This information is typically found in the tool's specifications, owner's manual, or by consulting the manufacturer.
- Identify Simultaneous Usage: This is a crucial step. It's rare for every single tool in a facility to run simultaneously at its peak consumption. Instead, focus on the tools and processes that are likely to operate concurrently during your busiest periods. Add up the CFM of all these simultaneously running tools.
- Incorporate a Safety Margin: Once you have the sum of your simultaneous CFM requirements, it's imperative to add a safety margin. This buffer accounts for potential future expansion, unexpected surges in demand, minor leaks in the system, or variations in tool performance over time. A common safety margin is 25%, but this can be adjusted based on the criticality of your operations and the likelihood of future growth.
Illustrative Example: Consider a typical workshop environment with the following pneumatic tools:
- Paint sprayer: This tool requires a consistent flow of 8 CFM for effective application.
- Impact wrench: Used for tightening and loosening fasteners, it consumes 5 CFM during operation.
- Sandblaster: A high-demand tool, the sandblaster utilizes 20 CFM to achieve its abrasive cleaning action.

If these three tools are anticipated to run simultaneously during peak production, the calculation would be:
8 CFM (Paint Sprayer) + 5 CFM (Impact Wrench) + 20 CFM (Sandblaster) = 33 CFM (Total Baseline)
Now, applying a standard 25% safety margin:
33 CFM * 0.25 (25% margin) = 8.25 CFM (Safety Margin)
33 CFM + 8.25 CFM = ≈ 41 CFM (Required Compressor Capacity)
Therefore, for this example, a compressor capable of consistently delivering approximately 41 CFM would be recommended to adequately meet the demands of simultaneous operation with a built-in safety net.
Professional Air Demand Audits for Precision:
While manual calculations provide a valuable starting point, for large-scale industrial operations or situations demanding absolute precision, onsite air demand audits are invaluable. Companies like IAS Texas specialize in these services, deploying advanced digital flow meters to meticulously monitor and record your actual air usage over a specified period.
This data-driven approach offers several significant advantages:
- Eliminates Guesswork: By measuring real-world consumption, the audit removes any assumptions or estimations, leading to a highly accurate assessment of your CFM needs.
- Optimized Compressor Sizing: The audit ensures your compressor is perfectly matched to your facility’s unique operational requirements, preventing both undersizing (leading to inadequate pressure and production bottlenecks) and oversizing (resulting in wasted energy and higher operating costs).
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: A precisely sized compressor operates at its most efficient point, reducing energy consumption and contributing to significant cost savings on your utility bills.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Beyond energy, an optimally sized system experiences less wear and tear, extending the lifespan of your compressor and minimizing maintenance expenditures.
- Identification of Leaks and Inefficiencies: During an audit, areas of air leakage or inefficient usage within your system can often be identified, allowing for corrective measures that further improve overall efficiency.
By understanding your airflow requirements with meticulous detail, whether through careful manual calculation or a professional air demand audit, you lay the groundwork for selecting an industrial air compressor that is not only powerful enough for your current needs but also efficient, reliable, and prepared for future demands.

Step 2: Determine Operating Pressure (PSI)
Next, identify your required pressure in PSI (Pounds per Square Inch).
Different industries and tools require different pressure levels:
- General manufacturing: 90–100 PSI
- Food & beverage: 120 PSI (for packaging or bottling)
- Medical / laboratory: 150–200 PSI for high-purity applications
Remember, more pressure = more power consumption. Overshooting your PSI by even 10% can increase energy costs by 5–8%.
IAS technicians calculate your exact PSI needs and design piping and dryer systems that minimize pressure drops, ensuring your compressor operates efficiently from day one.
Step 3: Consider Duty Cycle and Usage Patterns
The duty cycle determines how often your compressor runs relative to rest periods.
A 75% duty cycle means the compressor runs 45 minutes out of every hour.
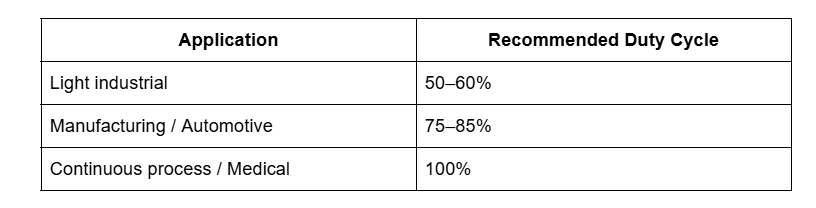
Oversizing the compressor for short bursts wastes energy, while undersizing leads to overheating and premature wear. IAS engineers help balance these factors to extend equipment life and reduce maintenance costs.
Step 4: Factor in Environmental Conditions
Texas temperatures can be brutal, and ambient heat, humidity, and altitude all affect compressor performance.
Hotter air is less dense, which means the compressor must work harder to deliver the same output.
IAS accounts for these variables when designing systems, selecting compressors with
proper cooling, ventilation, and filtration to handle Texas conditions.
Tip: Always install compressors in a well-ventilated, dry area to maintain efficiency.
Step 5: Plan for Future Expansion
Think beyond your current demand. If you plan to add machinery or extend your facility, size your compressor with 20–25% additional capacity to avoid replacing it later.
IAS Texas provides scalable system designs, including piping, dryers, and filters, that can easily expand as your operation grows.
Common Mistakes When Sizing a Compressor
Even experienced facility managers make these sizing errors:
1. Oversizing the system
A compressor that’s too large will cycle on and off frequently, wasting energy and wearing down internal components.
2. Ignoring leak losses
Leaks are silent energy killers. IAS recommends routine leak testing and aluminum air piping systems (learn more in our Aluminum Piping Guide) to minimize waste.
3. Forgetting about dryers and filters
Air treatment components cause small pressure drops. IAS always factors these into the sizing calculation to ensure your tools receive the right CFM at the right PSI.
The IAS Approach: Accurate, Efficient, and Turnkey
When you work with IAS Texas, you’re not just buying equipment; you’re getting a complete air system design solution.
Here’s how IAS ensures the perfect fit:
- Site Evaluation: Analyze current air usage and system layout.
- Data-Driven Audit: Measure CFM, PSI, and load patterns using advanced monitoring tools.
- System Recommendation: Match your demand with the ideal compressor model (fixed or variable speed).
- Installation & Commissioning: Professionally installed with dryers, filters, and aluminum piping.
- Maintenance Support: Preventive service plans to maintain peak efficiency.
IAS carries a range of high-performance air compressors, including rotary screw, oil-free, and VSD models, ideal for any industry.
Real-World Example: Right-Sized for Results
A fabrication facility in Houston struggled with frequent pressure drops and compressor overloads. After an IAS system audit:
- The old 40 HP unit was replaced with a 30 HP variable-speed compressor.
- Peak efficiency improved by 22%, and energy costs dropped by $3,600 annually.
- Operators reported
more stable air pressure across all workstations.
This demonstrates that accurate sizing leads to measurable savings, both in power and performance.
How IAS Ensures Energy Efficiency
IAS integrates air dryers, filters, and leak-free aluminum piping into every system to reduce pressure loss and extend compressor life.
Their holistic approach aligns with DOE Compressed Air System Best Practices, ensuring clients stay compliant and efficient.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I calculate what size compressor I need?
To determine the right compressor size, start by adding up the CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) requirements of every air tool or machine you plan to run at the same time. Then, multiply the total by 1.25 to allow for a 25% buffer that covers future demand and leak loss.
For example, if your tools use a combined 40 CFM, you’ll need a compressor rated for at least 50 CFM.
But sizing isn’t just about airflow, pressure (PSI), duty cycle; and environmental conditions also matter. That’s why many facilities rely on Industrial Air Services Texas (IAS) for a professional air audit and system design. IAS technicians use advanced monitoring tools to calculate real-world CFM and PSI requirements, ensuring your compressor is perfectly matched for efficiency and performance.
2. What does 2.6 SCFM at 90 PSI mean?
This specification tells you how much air the compressor delivers under standard conditions:
- SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per Minute) measures the air volume output.
- 90 PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) refers to the air pressure at which that output is produced.
So “2.6 SCFM at 90 PSI” means the compressor delivers 2.6 cubic feet of air per minute when operating at 90 pounds of pressure.
If your tools require more air than the compressor’s SCFM rating, you’ll experience power loss and slower performance. To avoid that, IAS Texas helps businesses match the SCFM rating to their actual air demand. Their engineers perform load testing and equipment analysis to ensure your system consistently delivers the air volume your tools need, no lag, no downtime.
3. How to calculate CFM for a compressor?
You can estimate your compressor’s CFM by dividing the air output (in cubic feet) by the time it takes to fill the tank. However, that’s just a rough estimate; real CFM depends on tank size, pressure settings, ambient temperature, and system leaks.
For precise measurements, IAS Texas offers on-site CFM testing and compressor performance audits using digital flow sensors. This ensures you’re getting accurate data for sizing, maintenance, or system upgrades.
IAS doesn’t just calculate, they design complete, energy-efficient air systems tailored to your facility. From compressor sizing to aluminum piping and filtration, IAS provides everything needed for long-term reliability and cost savings.
Get the Right Size, The First Time
Proper compressor sizing isn’t guesswork; it’s a science that impacts your bottom line. An oversized or undersized system can lead to energy loss, maintenance problems, and downtime.
Partner with Industrial Air Services Texas for expert analysis, professional installation, and long-term support. We’ll ensure your compressor system is accurately sized, energy-efficient, and built to last.
Ready to optimize your air system?
Request a free compressor
sizing consultation today and let IAS design the perfect solution for your facility.