Air Compressors 101: Types, Applications, and How IAS Helps You Choose the Right System
In industrial operations, compressed air is more than a utility; it’s the backbone of production. From manufacturing and machining to automotive, plastics, food processing, construction, and energy, compressed air powers the tools, automation, quality controls, and processes that drive daily output. When your air system goes down, your production stops. When your compressor runs inefficiently, your energy bill rises. When air quality is inconsistent, product quality suffers.
Choosing the right air compressor isn’t a simple matter of horsepower or price. It requires engineering, demand analysis, air quality planning, equipment sizing, and lifecycle support. This is why leading facilities across Texas invest in engineered systems backed by Industrial Air Services (IAS).
This guide breaks down the fundamentals of air compressors, how to select the right system, and how IAS provides the technical expertise and long-term support to maximise reliability, uptime, and ROI.
1. What Is an Air Compressor and Why Is It Essential?
An air compressor converts power into potential energy stored in pressurised air. That compressed air is used to:
- Power pneumatic tools
- Operate automation equipment
- Manage controls and actuators
- Support packaging and processing
- Maintain consistent production quality
- Drive HVAC and industrial processes
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, compressed air accounts for 10% of all electricity use in U.S. manufacturing facilities, making efficiency and reliability critical for controlling operational costs.
A properly designed compressed air system ensures:
- Stable PSI
- High-quality dry air
- Reduced energy waste
- Minimal downtime
- Long equipment lifespan
IAS ensures your system is sized, installed, and maintained correctly so you get maximum performance with minimum energy waste.
2. Types of Air Compressors (and When to Use Each)
Different facilities require different compressor technologies. Choosing the wrong type leads to inefficiency, moisture issues, and premature equipment failure.
Below are the primary industrial compressor types IAS installs and supports.
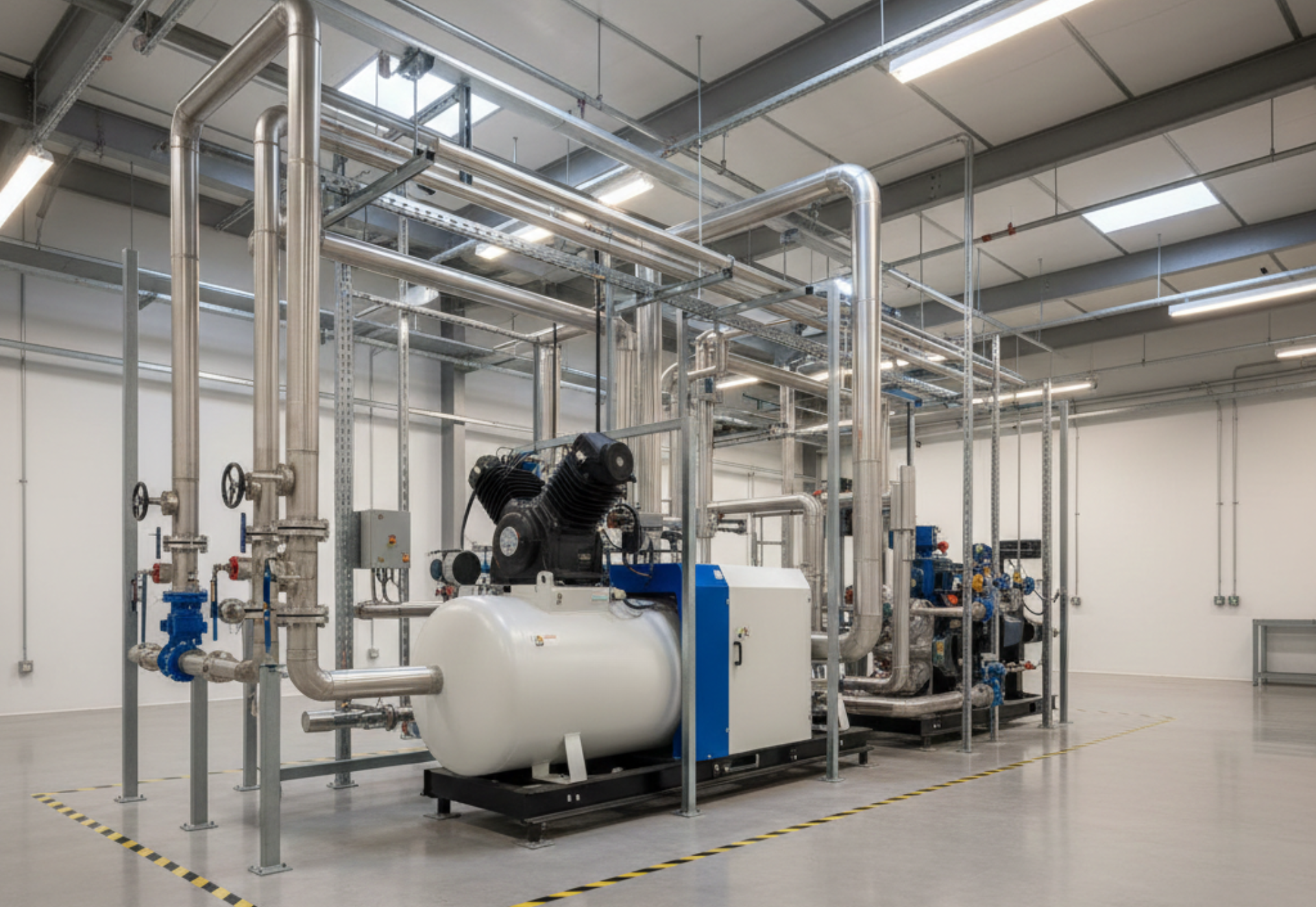
2.1 Rotary Screw Air Compressors (Most Common for Industrial Use)
Rotary screw compressors use two interlocking rotors to compress air. They are perfect for:
- Continuous-duty applications
- High-demand facilities
- Manufacturing plants
- Fabrication shops
- Automotive production
- Industrial automation
Advantages:
- High efficiency
- Quiet operation
- Continuous airflow
- Long lifespan
- Low maintenance
These are the workhorses of industry. If your plant runs full shift operations, you likely need a rotary screw system.

2.2 Reciprocating (Piston) Compressors
Piston compressors use a cylinder and a piston to compress air. They are ideal for:
- Low-to-medium demand
- Intermittent use
- Small shops or backup units
Advantages:
- Simple design
- Lower initial cost
- Good for short cycling
However, they are loud, require more maintenance, and are not efficient for continuous-duty applications.
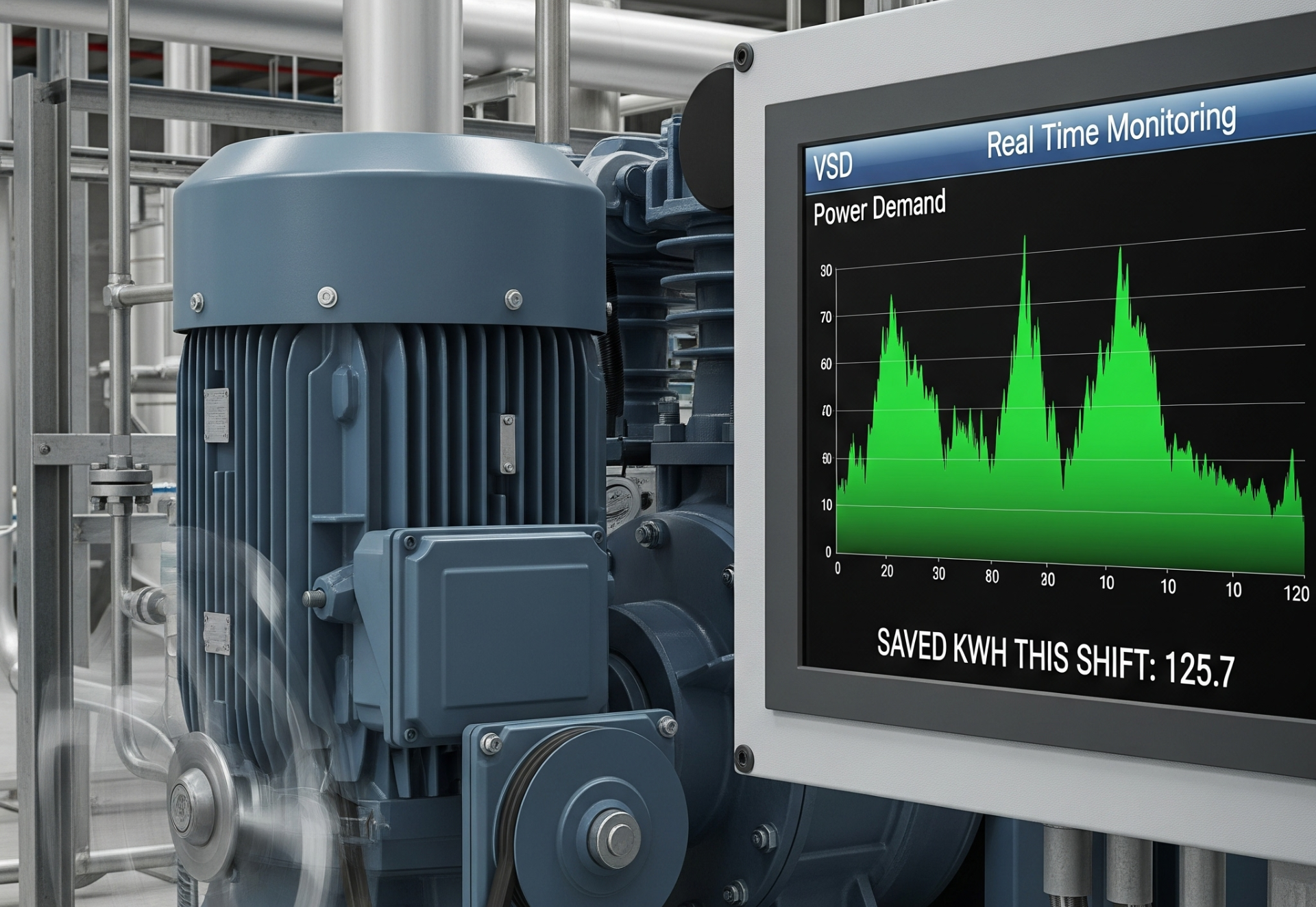
2.3 Variable Speed Drive (VSD) Compressors
A VSD compressor adjusts motor speed based on demand, reducing energy waste. These systems can cut power consumption by 20–40% compared to fixed-speed units.
Source:
Compressed Air & Gas Institute
Best for:
- Plants with fluctuating demand
- Multi-shift operations
- Facilities focused on energy savings
IAS engineers identify whether VSD technology can reduce your long-term operating costs and stabilise performance.
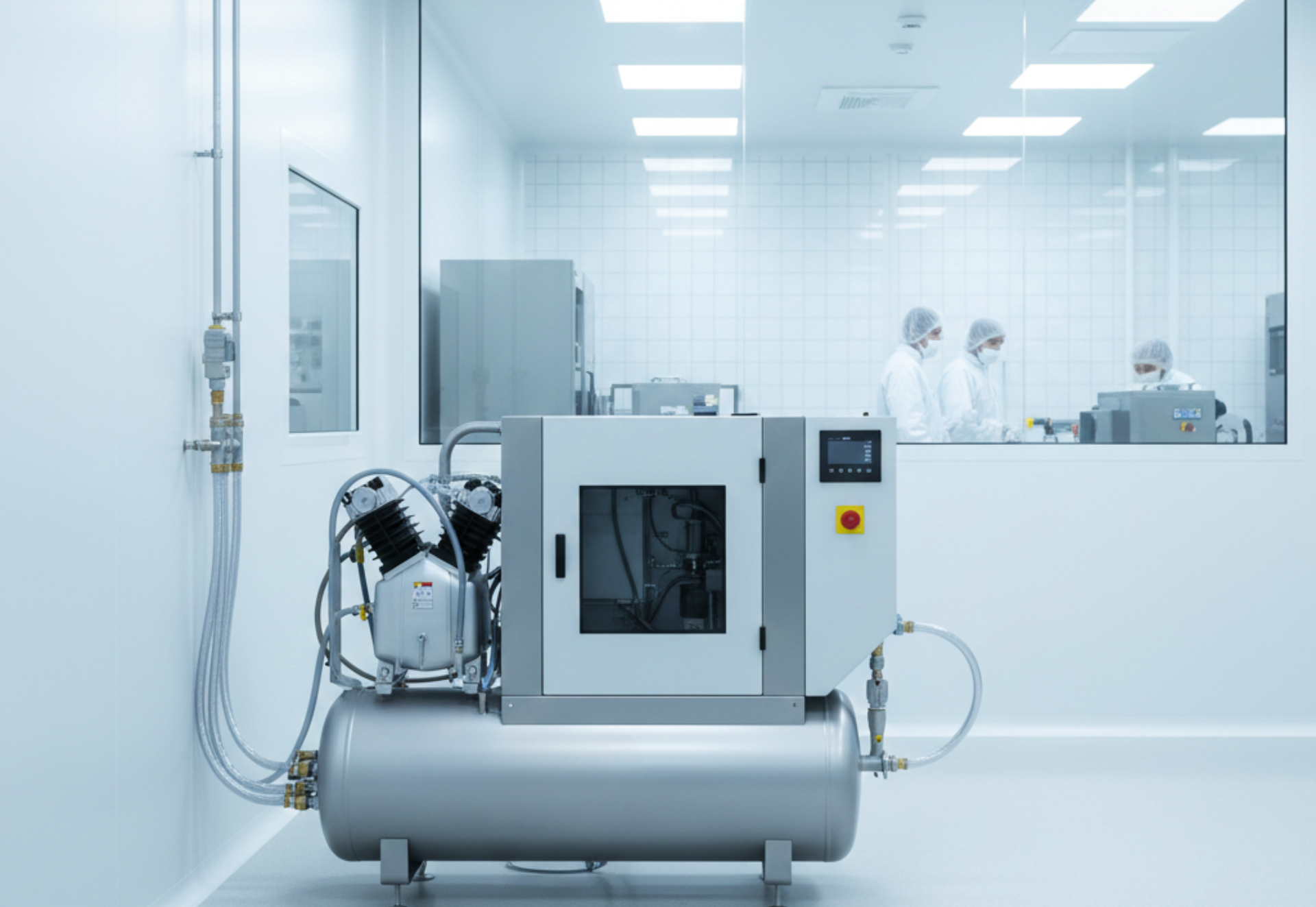
2.4 Oil-Free Compressors
Oil-free compressors deliver clean compressed air without lubrication inside the compression chamber. Industries requiring contamination-free air include:
- Food and beverage
- Pharmaceutical
- Medical
- Electronics
- Cleanroom manufacturing
Benefits:
- Zero oil contamination risk
- Compliant with ISO 8573-1 air quality standards
- Ideal for sensitive applications
External Reference:
ISO 8573 Air Quality Standards
IAS helps facilities determine whether they need oil-free or oil-injected systems based on regulatory and quality requirements.IAS plays a crucial role in assisting various industrial and manufacturing facilities with a critical decision: selecting the appropriate type of air compression system. This choice fundamentally boils down to determining whether an oil-free or an oil-injected (or oil-lubricated) system is necessary.
This determination is not arbitrary; it is driven primarily by stringent regulatory compliance mandates and the facility's specific product quality and purity requirements.
Oil-Injected Systems:
In these systems, oil is used within the compression chamber for lubrication, sealing, and cooling. They are generally more cost-effective to install and operate for applications where the presence of trace amounts of oil in the compressed air is permissible or where robust filtration can adequately mitigate the risk. However, they are unsuitable for sensitive processes.
Oil-Free Systems:
These compressors are specifically designed to deliver compressed air with absolutely no oil introduced into the compression process. This eliminates the risk of oil contamination in the final product or process stream. IAS strongly recommends oil-free systems for industries that:
- Operate under strict regulatory bodies (e.g., FDA, pharmaceutical GMPs): Regulations often prohibit the use of oil-lubricated equipment when the air comes into direct or indirect contact with ingredients, final products, or critical sterilisation processes.
- Require the highest level of air purity: This is non-negotiable for sectors like food and beverage production, pharmaceuticals, medical breathing air, electronics manufacturing, and certain advanced chemical processes where even minute oil aerosols can lead to costly batch spoilage, equipment malfunction, or health hazards.
By conducting a thorough assessment of the facility's operational environment, process demands, and adherence to ISO 8573-1 air quality standards, IAS helps facilities navigate these complex requirements to ensure the installed air compression system not only meets regulatory thresholds but also guarantees optimal production integrity and efficiency.
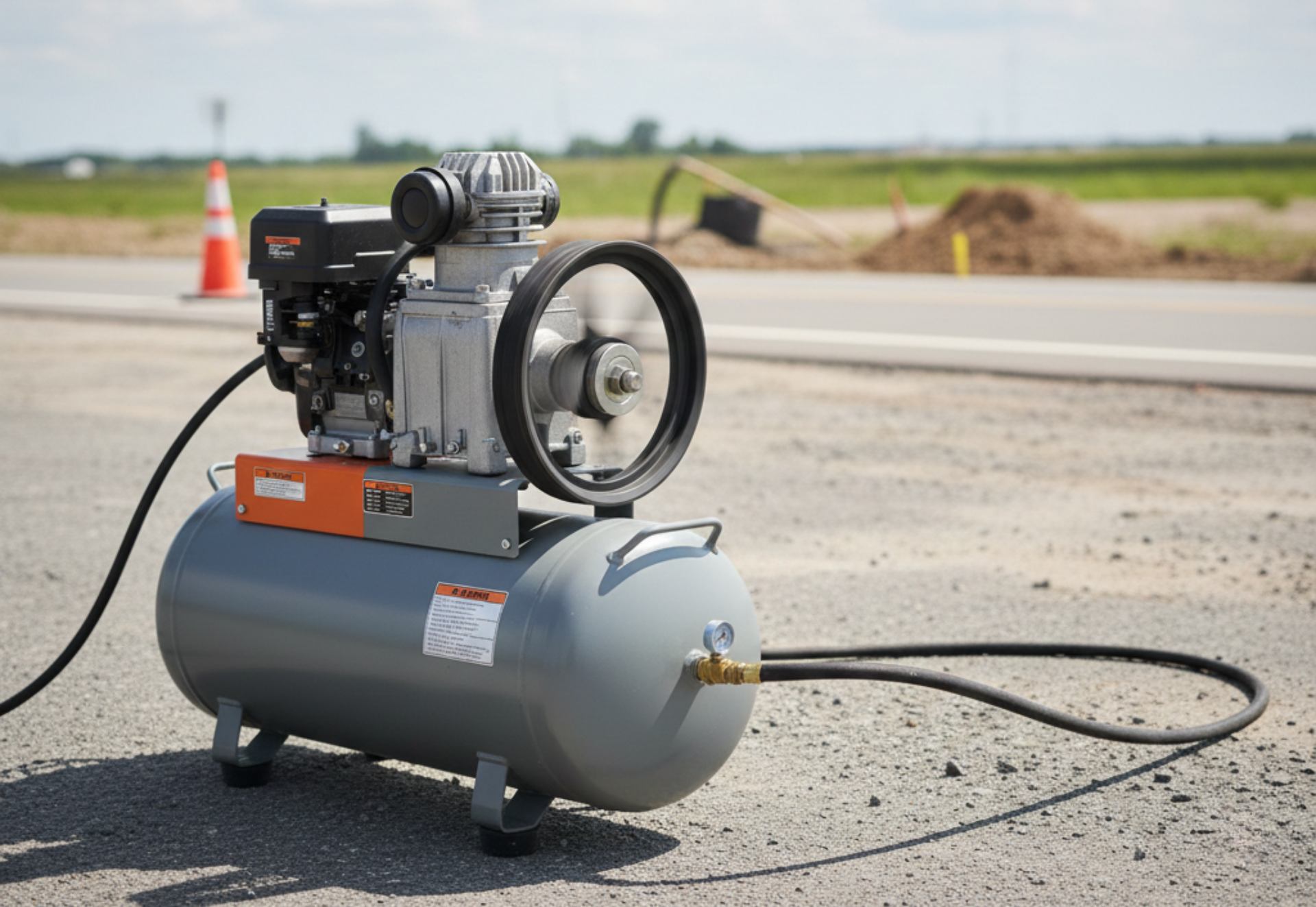
2.5 Portable Air Compressors
Used in:
- Construction
- Site maintenance
- Outdoor industrial settings
- Mobile operations
Portable units deliver flexibility where industrial mains-powered systems are not available.

3. How to Choose the Right Air Compressor (Engineering Criteria)
Most compressor failures come from incorrect sizing, not equipment brand. IAS prevents this with engineered selection.
Below are the key factors used to size and select the right system.
3.1 CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute)
The volume of airflow required. Every tool and process has specific CFM demands, and IAS calculates total facility demand, including:
- Peak load
- Continuous load
- Surge demand
- Future expansion
3.2 PSI (Pressure Requirements)
Different processes require different PSI levels. Undersized PSI reduces production efficiency. Oversized PSI wastes energy (and money).
3.3 Duty Cycle
How long must the compressor run?
- Indoor manufacturing: 80–100% duty cycle
- Automotive shops: 40–60%
- Construction: intermittent
IAS evaluates your real-world operating profile.
3.4 Air Quality Requirements (ISO Standard)
Air quality affects product quality, tool lifespan, and instrument safety. IAS chooses the right:
- Refrigerated dryer
- Desiccant dryer
- Filtration sequence
- Moisture separators
3.5 Electrical Capacity and Installation Space
Air compressors must fit your:
- Electrical supply
- Ventilation
- Ambient temperature
- Future expansion plans
Improper installation is one of the leading causes of overheating and breakdowns.
3.6 Energy Consumption
The DOE states that 70–90% of a compressor’s total lifecycle cost comes from electricity, not equipment cost.
Source: https://www.energy.gov/eere/amo
IAS engineers for efficiency, not just equipment sales.
4. Air Treatment: Dryers, Filters, and Storage
Compressed air quality is equally important as compressor performance.
4.1 Refrigerated Dryers
Best for general manufacturing and commercial use.
4.2 Desiccant Dryers
Required for:
- Pharmaceutical
- Petrochemical
- Cold environments
- High air quality
4.3 Filtration
IAS installs the correct filtration sequence:
- Particulate
- Coalescing
- Activated carbon
- High-efficiency filters
4.4 Storage Tanks
Essential for stabilising pressure, handling surge loads, and reducing cycling.
IAS evaluates the total system to ensure your air is dry, clean, and stable.
5. Why Maintenance Is Critical (And Why Most Failures Are Preventable)
A compressor is a long-term investment if maintained properly.
According to SMRP, preventive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime by 35–45%.
5.1 Common Failure Points
- Oil degradation
- Clogged filters
- Fouled coolers
- Overheating
- Moisture carryover
- Electrical faults
5.2 IAS Preventive Maintenance Includes:
- Lubricant replacement
- Filter and separator changes
- Dryer inspections
- Cooler cleaning
- Leak detection
- Belt and coupling inspection
- Electrical testing
- Pressure/flow monitoring
This is how IAS extends equipment lifespan and protects uptime.
6. How Industrial Air Services Supports Your Entire Compressed Air Lifecycle
IAS provides full-service support from selection to long-term care.
6.1 Sales & Engineering
- Air compressors
- Dryers
- Filtration
- Controls
- Storage tanks
6.2 Turnkey Installation
- Electrical
- Ventilation
- Piping
- Condensate systems
6.3 Preventive Maintenance
- Tailored PM programs
- Multi-year service plans
- Load analysis
- Thermal evaluations
6.4 Emergency Repair
Fast response when downtime threatens production.
6.5 System Optimisation
- Energy reduction
- Leak audits
- Air quality upgrades
- VSD integration
- Controls engineering
IAS keeps your air system reliable, efficient, and production-ready.
7. When Should You Contact IAS?
You should reach out if you observe:
- Pressure instability
- Moisture in lines
- Overheating
- Rising energy bills
- Frequent shutdowns
- Inconsistent air quality
- Compressor cycling issues
- Excessive noise or vibration
- Lack of maintenance support
IAS provides the engineering expertise to diagnose and correct these issues quickly.
Need a New Air Compressor or Service Partner? Trust IAS.
For engineering-based selection, installation, and service of industrial air compressors, partner with IAS.
Learn more: https://iastx.com/
Request an equipment
quote: https://iastx.com/
Schedule a system assessment: https://iastx.com/
Industrial Air Services supports manufacturers, warehouses, fabrication facilities, automotive shops, and industrial plants across Texas with reliable compressed air solutions built for uptime.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it worth owning an air compressor?
Yes. Owning an air compressor is highly valuable for manufacturing plants, workshops, automotive facilities, and commercial operations because it powers essential tools, automation, and production processes. A properly selected and maintained compressor improves efficiency, reduces downtime, and ensures consistent output.
IAS helps facilities choose, install, and maintain the right air compressor engineered for long-term performance.
Start here: https://www.iastx.com/
2. What tools can I use with an air compressor?
Air compressors can power a wide range of pneumatic tools, including impact wrenches, nail guns, grinders, sanders, spray guns, ratchets, inflators, blow guns, and various industrial automation tools. The key is choosing a compressor that meets the correct
CFM and PSI requirements for your tools.
IAS provides engineered sizing and system design to ensure your compressor matches your tool and process demands.
Get expert help: https://www.iastx.com/
3. What is important when buying an air compressor?
The most important factors include CFM, PSI, duty cycle, air quality requirements, energy efficiency, ambient temperature, and future production needs. Choosing the wrong size or type can lead to high energy bills, poor air quality, and equipment failure.
IAS performs on-site demand analysis and engineering to help you select the right compressor the first time.
Choose the right system: https://www.iastx.com/