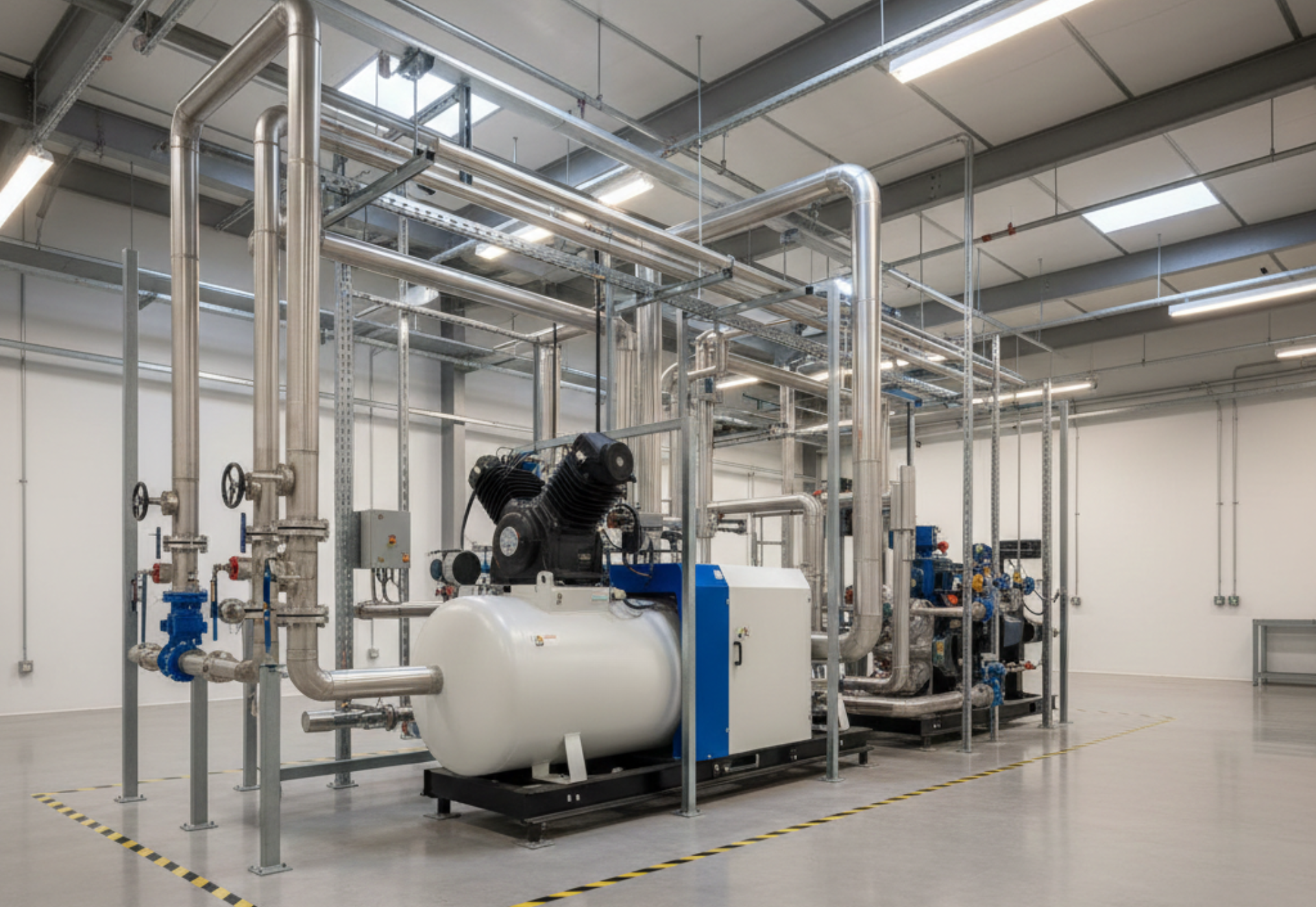
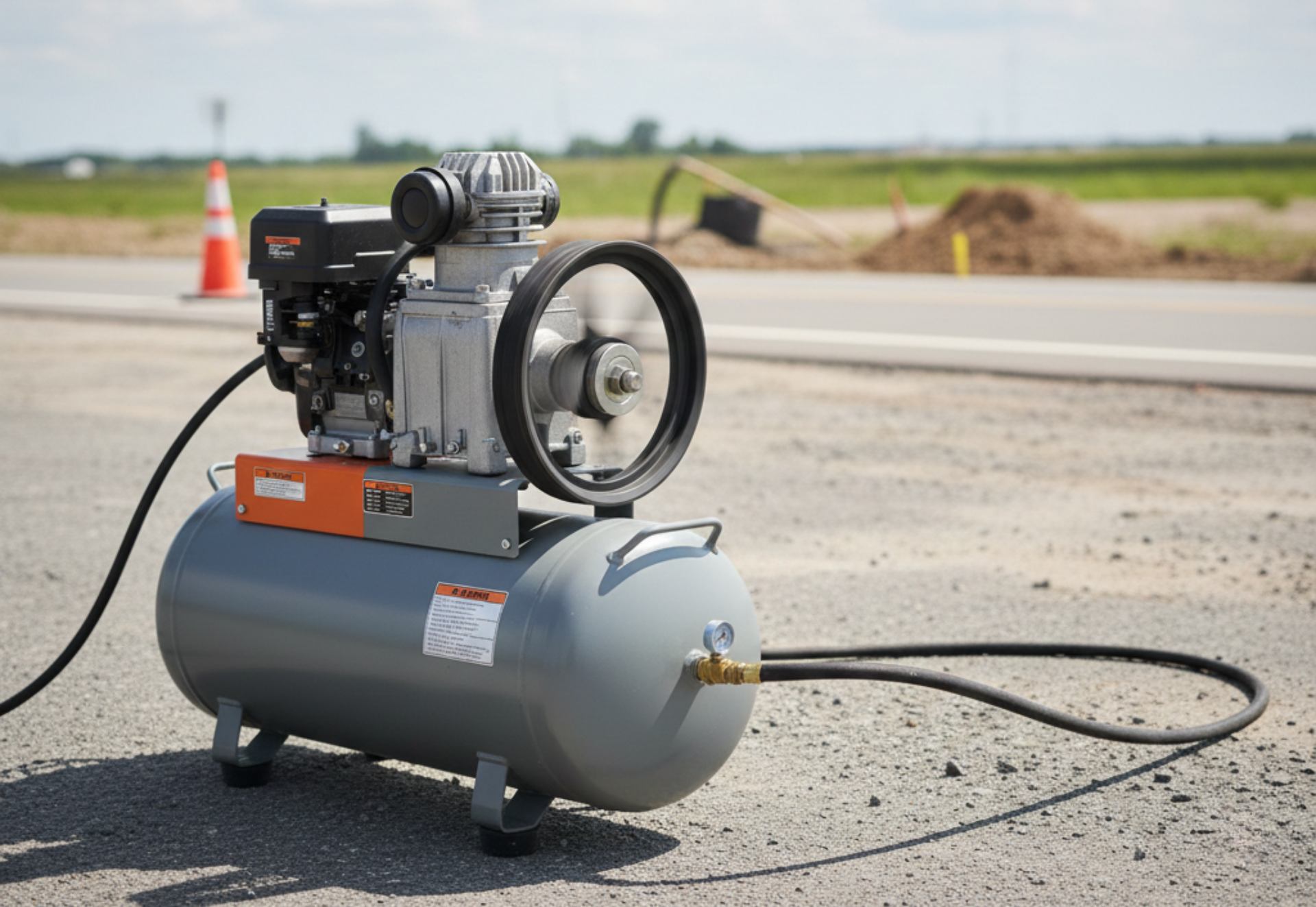
How to Choose the Right Air Compressor for Your Industrial Facility: Trends & Market Insights 2025
Compressed-air systems are the often-unsung backbone of modern industrial operations. Far from being a mere utility, they are critical to the seamless functioning of countless manufacturing processes. From powering precision pneumatic tools on assembly lines to driving the sophisticated automation systems that define modern factories, manufacturing plants rely on compressed air for everything from the initial stages of production and meticulous packaging to the final finishing touches on products. This pervasive reliance means that the strategic choice of the right air compressor, coupled with diligent management, can have a profound and direct impact on a plant’s operational uptime, significantly influence energy costs, and ultimately affect the quality and consistency of the final product. A Growing Market: Trends and Projections
The global air-compressor market is a substantial and rapidly expanding sector. Valued at approximately
USD 26.57 billion in 2024, it is projected to grow significantly to
around USD 40.15 billion by 2033, demonstrating a robust Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.7%. These impressive figures, based on detailed analysis by
Grand View Research, underscore the increasing global demand for reliable compressed air solutions. A substantial portion of this growth is concentrated in the Asia-Pacific region, which alone accounts for more than 42% of the market share as of 2024, highlighting its critical role in global manufacturing and industrial expansion. Strategic Importance Beyond Technicalities
Given the sheer scale and critical nature of compressed-air systems, the selection, operation, and maintenance of air compressors must be viewed as strategic imperatives, not merely as technical considerations. The decisions made in these areas can have long-term implications for a company's profitability, efficiency, and competitive edge.
This comprehensive guide aims to equip industrial professionals with a clear roadmap for navigating this essential aspect of industrial operations. We will delve into:
- Market Trends: An in-depth look at the current dynamics shaping the air compressor industry, including technological advancements and regional growth drivers.
- Types of Compressors: A detailed exploration of the various compressor technologies available, from rotary screw to reciprocating, and their respective applications and benefits.
- How to Pick the Right One: Practical methodologies and considerations for selecting the optimal air compressor that aligns with specific industrial needs, energy efficiency goals, and operational demands.
- Maintenance & Service Strategies: Best practices for ensuring the longevity, reliability, and peak performance of air compressor systems, including preventative maintenance, predictive analytics, and service agreements.
- What’s Coming Next: An outlook on future innovations and emerging technologies in compressed air, preparing businesses for the next generation of industrial efficiency.
Whether you are in the crucial phase of specifying new equipment for a greenfield facility, planning a strategic upgrade to enhance an existing system, or seeking to optimize the performance and efficiency of your current compressed air infrastructure, this article provides the essential insights and guidance needed to make informed decisions and drive operational excellence.
1. Market Landscape & Key Trends
Growth & Regional Insights
- The global air-compressor market size was estimated at USD 26.71 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach around USD 42.4 billion by 2034, growing at ~4.7% CAGR from 2025-2034. According to Precedence Research.
- Asia-Pacific dominates with a ~42.4% market share in 2024.
- In the U.S., the air-compressor market is valued at USD 3.39 billion in 2024, with a slower growth (~3.4% CAGR from 2024-2030). These numbers underscore that compressed-air systems remain a large, steadily growing segment of industrial equipment, especially in manufacturing-intensive regions.
Key Drivers
- Energy efficiency demands: As energy costs rise and regulatory pressure increases, industrial buyers look for compressors with better efficiency (e.g., variable-speed drives, leak detection).
- Expansion of automation & manufacturing: Growth in sectors like food & beverage, electronics, and automotive pushes demand for reliable compressed air.
- Emerging markets growth: Industrialization in Asia, Latin America, and other regions is increasing equipment deployment.
- Service and lifecycle focus: Buyers increasingly value service, reliability, and uptime—not just purchase price.
Challenges
- Rising electricity costs and pressure to reduce carbon footprint.
- Supply-chain constraints for large equipment, parts, and commissioning.
- Need for qualified technical support, especially in remote locations.
- Legacy systems with poor efficiency or high leakage remain difficult to upgrade.
Mini Snapshot / Case-Call-out
For example, a manufacturing plant in Asia replaced a fixed-speed compressor with a VSD unit, sealed air leaks, and reported a ~20–25 % energy reduction within a year. (While precise numbers vary, many industry sources suggest this range.)
Also, as per some reports from Zion Market Research, the oil-free compressor market alone is projected to reach USD 51.15 billion by 2032 (CAGR ~6%).
See our earlier blog on “Top Maintenance Tips to Extend Your Air Compressor’s Life”

2. Types of Air Compressors & Their Uses
Common Types
Here’s a breakdown of the typical compressor types and where they fit:
- Reciprocating (piston): Suitable for lower-capacity, intermittent duty and smaller plants.
- Rotary-screw (oil-flooded or oil-free): The workhorse for many industrial operations; supports continuous duty.
- Centrifugal (dynamic): Used for very high flow/large-scale compressed air systems (e.g., heavy manufacturing).
In lubrication terms: - Oil-flooded (oil-lubricated): Uses oil in the compression chamber; higher efficiency and longevity under heavy load.
- Oil-free (or oil-injected/sealed): No oil in the air stream; required when air purity is critical (food, pharma, electronics).
Usage & Application Examples
- In general manufacturing (metal forming, automotive), oil-flooded rotary screws are common due to high performance under continuous duty.
- In food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, or electronics manufacturing, oil-free compressors are preferred because of contamination risk from oil. Based on the article published by Air Compressor Ohio.
- Portable compressors or site construction may use smaller reciprocating or portable screw units.
Comparison Table

Picking the Right Type
For example, if your facility produces pneumatic tools and operates with moderate duty, a rotary-screw oil-flooded unit may be ideal. Conversely, if you run a clean room with sensitive electronics or pharmaceuticals, you may need an oil-free compressor despite the higher cost.
Explore our product page comparing “Stationary vs Portable Compressors”.
For an in-depth comparison of oil-free vs oil-flooded, see “Oil-Free vs Oil-Flooded Compressed Air Systems: Which is Best for Your Operation?”
3. How to Choose the Right Air Compressor for Your Needs
Selecting the correct compressor is more than picking the largest machine. Consider the following decision criteria:
Key Decision Factors
- Required pressure & flow: Determine your system’s demand profile (CFM or m³/h at a certain bar/PSI).
- Duty cycle & operating hours: Will it run continuously or intermittently?
- Footprint & installation environment: Space, ventilation, ambient temperature, noise.
- Air quality requirements: Does your process need oil-free, dew point, sterile air?
- Energy efficiency metrics: Look for kW per 100 CFM, VSD options, etc.
- Maintenance & service accessibility: Consider ease of maintenance, availability of parts, and local service.
- Total cost of ownership (TCO): Purchase cost is only part of the equation—energy consumption and downtime dominate lifetime cost.
Lifecycle Cost Matters
Many plants find that a poorly matched compressor or an under-maintained system results in high energy bills and downtime. Upgrading to a VSD unit and sealing air leaks, for example, can yield 20–30% energy savings in many cases.
Checklist for procurement:
- Map out current and future compressed-air demand.
- Include a 10–20% growth buffer for expansion.
- Review the supplier’s efficiency ratings and case studies.
- Confirm service network, spare parts lead time, and commissioning support.
Ask about training, monitoring option,s and maintenance contract offerings.
Procurement Tip
Don't forget to ask about after-sales service: the availability of trained technicians, local parts, and scheduled preventive maintenance can mean the difference between uptime and costly downtime.

4. Maintenance & Service Strategies
Even the best compressor fails to deliver if not maintained properly. Maintenance and service are critical for ensuring longevity, efficiency, and uptime.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
- Daily: Check for air leaks, check pressure drop across filters, and monitor ambient temperature.
- Monthly: Inspect filters (air intake, separators), check oil levels (for oil-flooded), check belts/hoses, and system connections.
- Annually: Full service — change oil/separators/filters, inspect motor bearings, measure system efficiency, review air-leak audit.
Industry reports show that compressed-air leaks can account for 20-30% of air consumption if unchecked, leading to energy waste.
Why Service Partnership Matters
Selecting a supplier who offers both sales
and service gives you continuity: easier parts, faster response, better system optimization.
Regular service helps:
- Maintain efficiency (reducing energy consumption)
- Prevent unplanned downtime
- Extend equipment life
- Keep air quality consistent (especially for oil-free systems)
KPI Tracking
Encourage your plant to track:
- Uptime (% of available time)
- Mean time between failures (MTBF)
- Energy consumption per 100 CFM
- Number and cost of service events
- Spare parts usage and cost
These help benchmark performance, optimize service intervals, and justify upgrades.
5. Innovations & Future Outlook
Staying ahead in compressed-air technology ensures your operations remain efficient, adaptable, and competitive.
Smart & Connected Systems
The rise of IoT and Industry 4.0 is enabling compressors with real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and performance-based service contracts.
For example, AI-enabled sensors can detect early bearing wear or abnormal vibration, triggering service before failure occurs.
Sustainability & Efficiency
- Oil-free compressors are increasingly adopted in industries requiring ultra-clean air (pharma, electronics) because they minimize contamination risk and reduce the disposal of used oils.
- Variable-Speed Drive (VSD) technology responds to demand fluctuations, reducing wasted energy.
- Lifecycle assessments and carbon-footprint considerations are becoming part of procurement decisions.
Market Forecast & Emerging Applications
- Some forecasts project the industrial air-compressor market will reach
USD 65.66 billion by 2031, growing at ~7.8% CAGR. According to
Globe News Wire.
- Emerging applications: electric-vehicle manufacturing, hydrogen production, large-scale clean-room manufacturing, smart factories.
- As production becomes more agile and decentralized (e.g., micro-factories), flexible compressed-air solutions (variable speed, modular, portable) will gain traction.
Optimizing your industrial facility's compressed-air system is crucial for operational efficiency and cost control. While often overlooked, these "behind-the-scenes" systems directly influence uptime, energy consumption, air quality, and overall expenses. A strategic approach, focusing on selecting the right compressor type, matching it to specific duty cycles and process requirements, and implementing proper maintenance, yields significant returns, far beyond simply purchasing the cheapest equipment.
To effectively optimize your compressed-air system, consider the following key aspects:
- Understanding Your Compressed-Air Demand: A thorough assessment of your facility's compressed-air needs is the foundational step. This involves precisely determining the required flow (volume of air needed), pressure (force at which the air is delivered), and duty cycle (how often and for how long the compressor operates). Accurate demand assessment prevents oversizing or undersizing, both of which lead to inefficiencies and increased costs.
- Choosing the Right Compressor Type: The industrial landscape offers a variety of compressor technologies, each with distinct advantages. Key considerations include:
- Oil-free vs. Oil-flooded: Oil-free compressors are essential for applications requiring pristine air quality, such as in food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and medical industries, where even trace amounts of oil contamination are unacceptable. Oil-flooded compressors are generally more robust and cost-effective for applications where air purity is not a critical concern.
- Screw vs. Reciprocating: Rotary screw compressors are ideal for continuous, high-volume air demand due to their efficiency and smooth operation. Reciprocating (piston) compressors are better suited for intermittent use and applications requiring high pressure, offering good efficiency at partial loads.
Evaluating the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): The initial purchase price of a compressor represents only a fraction of its true cost over its lifespan. A comprehensive TCO analysis should include:- Energy Consumption: This is often the largest component of TCO, as compressors are significant energy consumers. Modern compressors with variable speed drives (VSD) can offer substantial energy savings by adjusting output to match demand.
- Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance, including filter changes, oil checks, and preventative servicing, is essential for longevity and efficiency. Consider the cost of spare parts and technician labor.
- Downtime Costs: Unexpected breakdowns can lead to significant production losses and associated expenses. Reliable equipment and proactive maintenance minimize this risk.
Partnering with a Reputable Supplier: The relationship with your compressor supplier extends beyond the initial purchase. A strong partnership should include:- Service and Support: Access to qualified technicians for routine maintenance, emergency repairs, and technical advice is crucial.
- Spare Parts Availability: Ready access to genuine spare parts minimizes downtime during repairs.
- Long-term Support: A supplier committed to long-term support can provide valuable insights and assistance as your operational needs evolve.
Monitoring, Maintaining, and Upgrading: A compressed-air system is not a static installation. Continuous optimization is key:- Monitoring: Regularly monitor air quality, pressure, flow, and energy consumption to identify inefficiencies and potential issues.
- Maintenance: Implement a rigorous preventative maintenance schedule to ensure peak performance and extend equipment life.
- Upgrades: As your industrial processes evolve, your compressed-air system may need upgrades or modifications to meet new demands or incorporate more energy-efficient technologies.
Ready to take the next step towards an optimized compressed-air system?
Contact our team today for a
free site audit and recommendation. We offer a comprehensive evaluation of your current setup, provide a customized equipment evaluation, and deliver a detailed quote. Additionally, you can check our "Air Compressor Selection Blogs" to guide your decision-making process.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the most common cause of air compressor failure?
The most common cause of air compressor failure is poor maintenance, particularly neglecting oil changes, air filter replacements, and system inspections. Over time, dirt buildup, oil contamination, and unchecked air leaks can reduce compressor efficiency, leading to overheating or motor failure.
At Industrial Air Services Texas (IAS), we help clients avoid costly downtime through preventive maintenance programs tailored to your compressor type and usage. Our team performs scheduled inspections, performance diagnostics, and genuine parts replacement to ensure your air compressor operates at peak efficiency for years.
Learn more about our compressor service and maintenance programs at iastx.com.
2. Which air compressor brand lasts the longest?
Longevity depends on the brand’s engineering quality and consistent maintenance. Leading brands such as Kaeser, Ingersoll Rand, and Atlas Copco are known for durability, but even top-tier equipment can fail prematurely without proper care. That’s why IAS partners with trusted compressor brands and provides factory-certified service for most major manufacturers. Our expert technicians ensure your system runs like new, whether you need rotary screw, oil-free, or portable air compressors.
Seeking a reliable compressor or OEM parts? Explore our full product lineup at iastx.com.
3. How much does a compressor cost?
The cost of an air compressor can vary widely depending on type, capacity, and features:
- Small industrial units: start around $3,000–$5,000
- Mid-range rotary screw compressors: range between $8,000–$20,000
- Large-scale industrial systems: can exceed $30,000+, depending on configuration and automation level
At Industrial Air Solutions Texas, we don’t just sell compressors; we help you find the right model that fits your production needs and budget. We also offer competitive pricing, installation support, and after-sales service to help your business maximize ROI and uptime.
Request a custom quote or speak to an IAS specialist today via iastx.com/contact